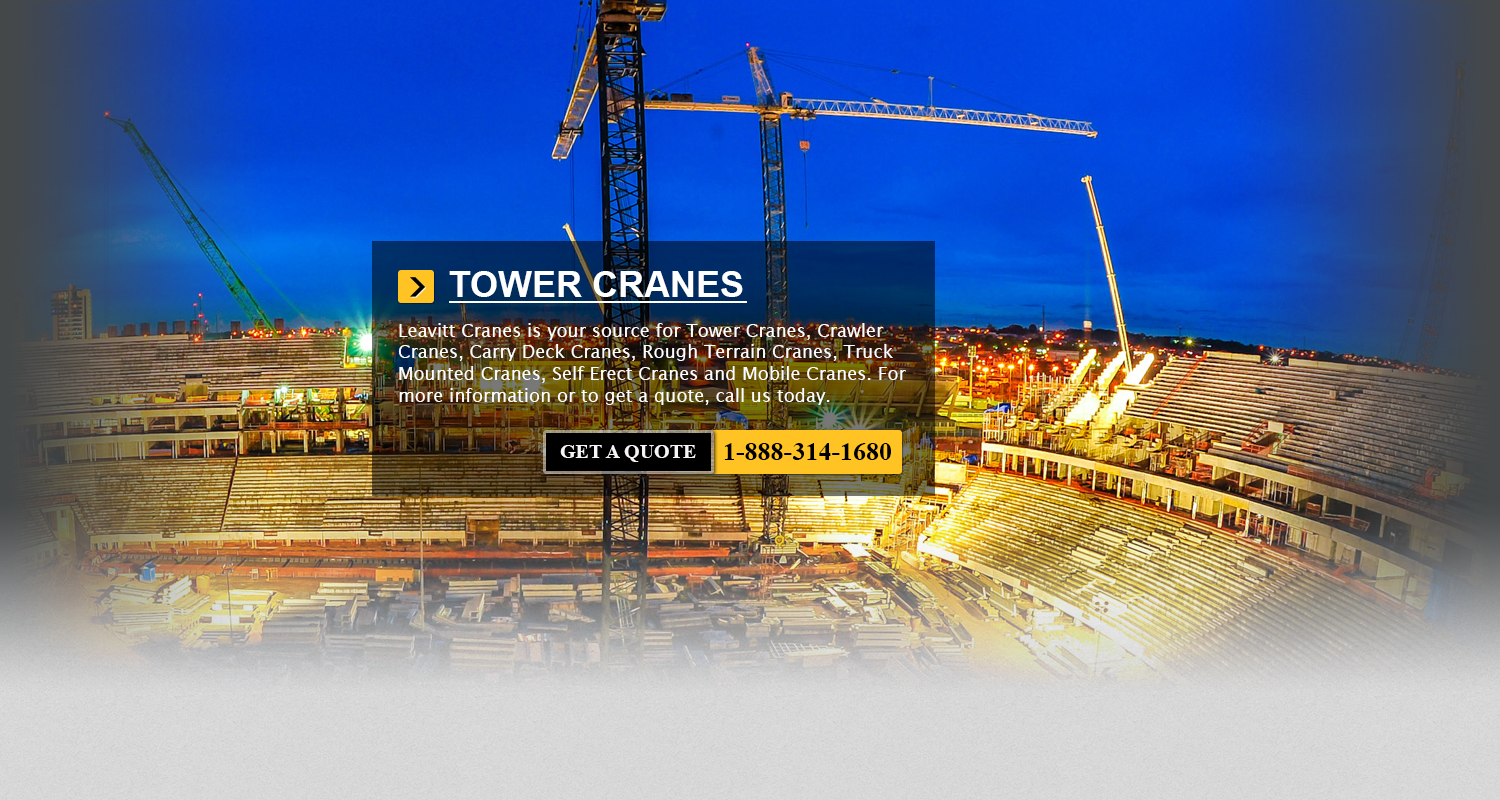
JCB Aerial Lifts San Francisco
Aerial Work Platforms
The aerial work platform or AWP is a machinery engineered and designed to raise workers and tools to a certain height for the completion of jobs. The type of machinery varies with the specific make and unit. Before aerial work platforms were developed, all tasks requiring work at high levels had to be done with scaffolding. Hence, the invention of aerial work platforms has kept a lot of employees safe and increased the overall productivity of similar tasks.
There are 3 key types of aerial work platforms. They are scissor lifts, boomlifts and mechanical lifts. These kinds of equipment could be operated with pneumatics, mechanically utilizing a pinion and rack system or by hydraulics or with screws. These models may be self-propelled with controls located at the platform, they may be unpowered units which require an external force to move them or be mounted to a vehicle so as to be transported.
The aerial work platform was created by John L. Grove, an American inventor and industrialist. Nonetheless, during 1966, before JLG's very first model, a company known as Selma Manlift introduced an aerial lift unit.
In 1967, after selling his previous business Grove Manufacturing, John L. Grove along with his wife decided to take a road trip. They decided to make a stop at Hoover Dam. While the couple was there, Grove unfortunately saw 2 employees electrocuted while they were working on scaffolding. This terrible incident led John Grove to discover an untapped market for a new product that could safely raise workers in the air for them to perform maintenance and construction tasks in a better way.
John bought a small metal fabrication company and formed a partnership along with 2 friends, once he returned home from his vacation. The small business immediately started designing ideas for the aerial work platform. The new business was called JLG Industries Inc. They proudly launched their very first aerial work platform during the year 1920 with the aid of 20 workers.
- Terex Man Lifts San Francisco
Terex Manlift Specifications Terex is a Westport, Connecticut company which specializes in making in manufacturing construction machinery. Machines such as manlifts, boom lifts and aerial lifts. These types of machines are designed to facilitate access... More - Haulotte Rough Terrain Scissor Lifts San Francisco
Traditionally, industrial lifts have been used in production and manufacturing settings to raise and lower work things, people and materials. The scissor lift, also referred to as a table lift, is an industrial lift which... More - JLG Zoom Boom San Francisco
To handle all of your rough terrain difficulties, JLG offers the 400 Series and its fastest drive and lift speeds in its class which will ensure a boost in production. You would be able to... More - Omega Rough Terrain Forklifts San Francisco
MEGA Series - The MEGA Series is a powerful lift truck which is capable of covering a variety of applications. From steel and lumber and dealing with other kinds of heavy lifting as much as... More - Toyota Counterbalance Forklift San Francisco
For over 4 decades, Toyota has been among the leading suppliers of innovative lift trucks in the industry. Up to date, the business has sold more than 1 million forklifts. The company has earned a... More